Meaning of Plant Layout:
Plant layout is a “technique of locating different machines and plant services within the factory so that the greatest possible output of high quality at the lowest possible total cost can be available”.
"A good layout results in comforts, convenience, appearance, safety, and profits. A poor layout results in congestion, waste, frustration, and inefficiency.”
Plant layout is a “technique of locating different machines and plant services within the factory so that the greatest possible output of high quality at the lowest possible total cost can be available”.
"A good layout results in comforts, convenience, appearance, safety, and profits. A poor layout results in congestion, waste, frustration, and inefficiency.”
Objectives of PLANT LAYOUT:
- Should provide overall satisfaction to all concerned.
- Material handling and internal transportation from one operation to the next is minimized and efficiently controlled.
- The production bottle necks and points of congestions are to be eliminated so that input raw materials and semi-finished parts move fast from one work station to another.
- Should provide high work in process turnover.
- Should utilize the space most effectively; may be cubical utilization.
- Should provide worker’s convenience, promote job satisfaction and safety for them.
- Should avoid unnecessary investment of capital.
- Should help in effective utilization of labour.
- Should lead to increased productivity and better quality of the product with reduced capital cost.
- Should provide easy supervision.
- Should provide space for future expansion of the plant.
- Should provide proper lighting and ventilation of the areas of work stations.
Factors for PLANT LAYOUT:-
- Location of departments.
- Type of product, method of production, production process.
- Production capacity.
- Type of industry, like synthetic, analytic, conditioning or extractive.
- Grouping of machines.
- Material flow pattern.
- Space requirement for machines, work area, material handling, storage, and other facilities.
- Safety factors.
- Health and other factors, like ventilation, natural light, removal of smoke, and fumes etc.
- Provision for future expansion.
- Flexibility for future modifications due to diversification, technology, or product design changes.
- Storage system i.e., centralised or decentralised or a combination of both.
Principles of PLANT LAYOUT:
While designing the plant layout – the following principles must keep in view:
Movement: Materials and labour should move over minimum distances which makes in saving cost and time of transportation and material handling.
Space Utilization: All available cubic space should effectively utilize – both horizontally and vertically.
Flexibility: Layout should be flexible enough to be adaptable to changes required by expansion or technological development.
Interdependence: Interdependent operations and processes should locate near each other; to minimize product travel.
Overall Integration: All the plant facilities and services should fully integrate into a single operating unit – to minimize the cost of production.
Safety: There should be an in-built safety measures to get overcome to any hazard.
While designing the plant layout – the following principles must keep in view:
Movement: Materials and labour should move over minimum distances which makes in saving cost and time of transportation and material handling.
Space Utilization: All available cubic space should effectively utilize – both horizontally and vertically.
Flexibility: Layout should be flexible enough to be adaptable to changes required by expansion or technological development.
Interdependence: Interdependent operations and processes should locate near each other; to minimize product travel.
Overall Integration: All the plant facilities and services should fully integrate into a single operating unit – to minimize the cost of production.
Safety: There should be an in-built safety measures to get overcome to any hazard.
Types of PLANT LAYOUT
- Product or Line Layout:
If all the processing equipment and machines are arranged according to the sequence of operations of the product, the layout is called product type of layout. In this type of layout, only one product of one type of products is produced in an operating area. This product must be standardized and produced in large quantities in order to justify the product layout. - Process or Functional Layout:
The process layout is particularly useful where low volume of production is needed. If the products are not standardized, the process layout is more low desirable, because it has creator process flexibility than other. In this type of layout, the machines and not arranged according to the sequence of operations but are arranged according to the nature or type of the operations. - Fixed Position Layout:
This type of layout is the least important for today’s manufacturing industries. In this type of layout the major component remain in a fixed location, other materials, parts, tools, machinery, man power and other supporting equipment’s are brought to this location. The major component or body of the product remain in a fixed position because it is too heavy or too big and as such it is economical and convenient to bring the necessary tools and equipment’s to work place along with the man power. This type of layout is used in the manufacture of aircrafts ships etc. - Combination Layout:
Now a days in pure state any one form of layouts discussed above is rarely found. Every layout has got certain advantages and limitations. Therefore, industries would to like use any type of layout as such. Flexibility is a very important in factory, so layout should be such which can be molded according to the requirements of industry, without much investment. If the good features of all types of layouts are connected, a compromise solution can be obtained which will be more economical and flexible.
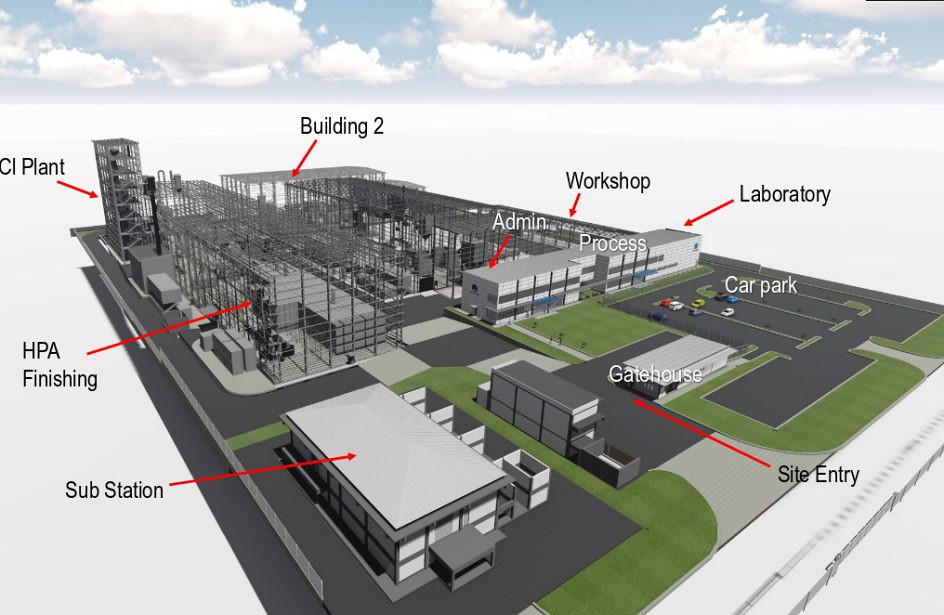
Diagram Representation of PLANT LAYOUT







Thank you ma'am
ReplyDelete